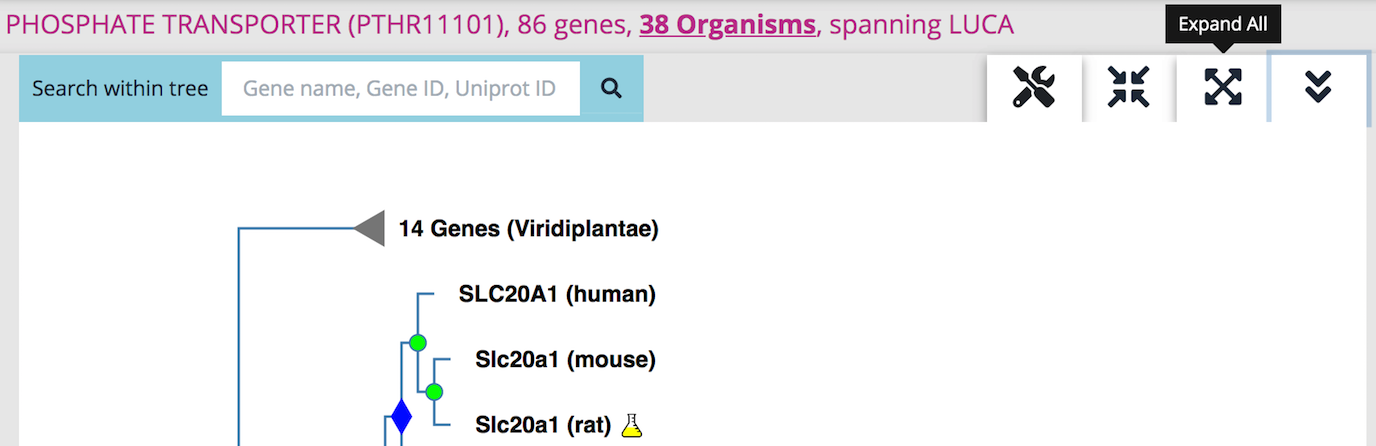
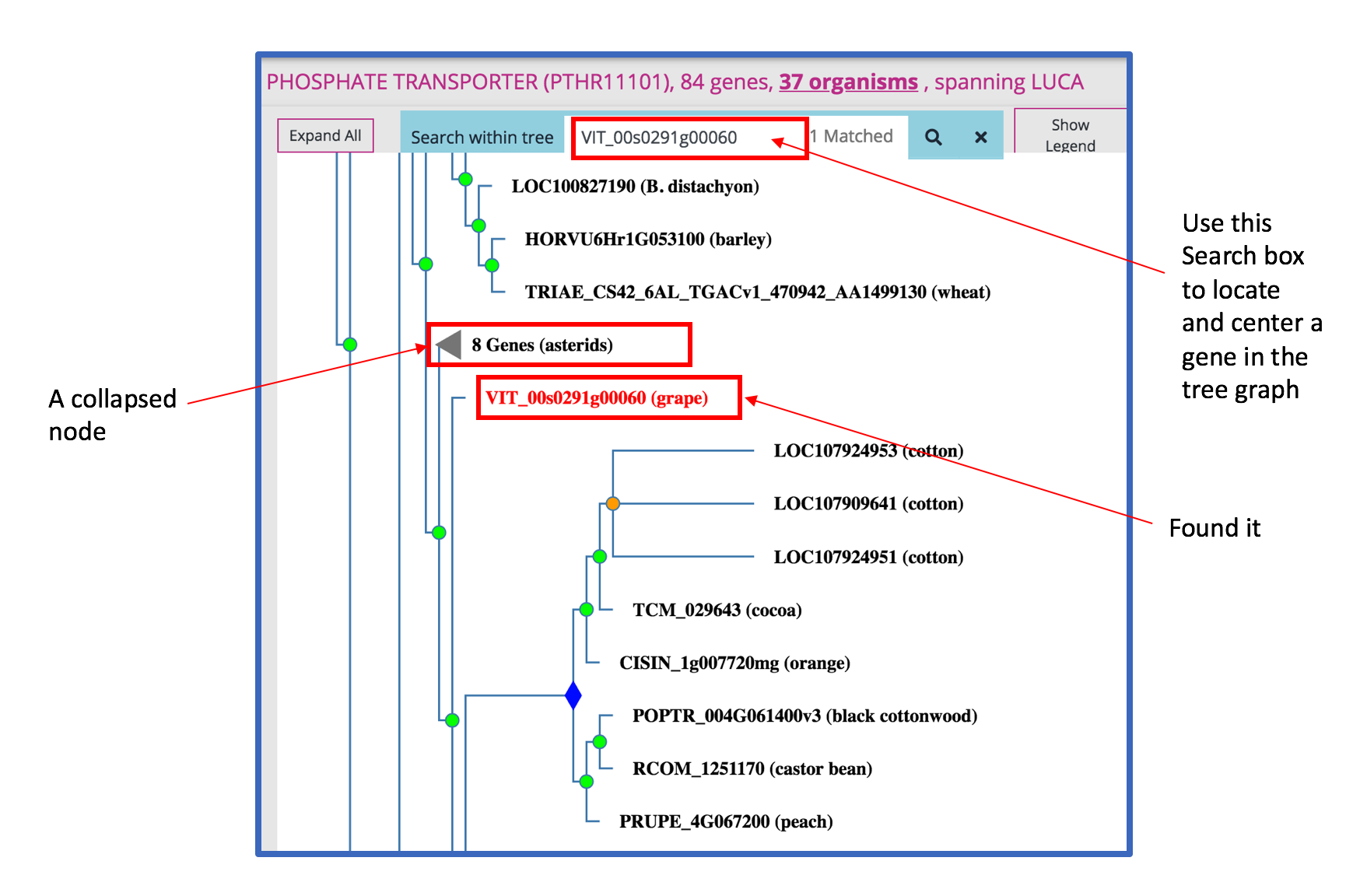
The default display of a gene tree in Phylogenes is a 'Compact view'. The compact view displays all gene(s) with known functions and collapses branches containing genes with no known functions. A gene with a known function is one that is annotated to at least one GO term and supported by experimental evidence. If a gene family does not have any gene with any known function we display node(s) of first duplication event(s) and collapse all its children nodes. A first duplication event here refers to an internal node that is a duplication event and that none of its ancestral internal nodes is a duplication event.
Click on the 'Expand All' icon to see a fully expanded tree.

Types of nodes:
A leaf node, the very end of a horizontal branch, is labeled as "gene name, or gene id if gene name is not provided (species name)". For example, DET2 (tomato), HORVU2Hr1G019650 (barley).
An internal node or the root node can be either a speciation (GREEN circle), duplication (ORANGE circle), horizontal transfer (CYAN circle) event, or a subfamily node (BLUE diamond). A subfamily is a group of genes that share a particularly high degree of similarity due to limited divergence from their common ancestor. Genes in a subfamily are, in general, closely-related orthologs. More about subfamily

Branch length:
The displayed horizontal branch lengths are scaled with calculated branch lengths.
In a tree graph, you can:
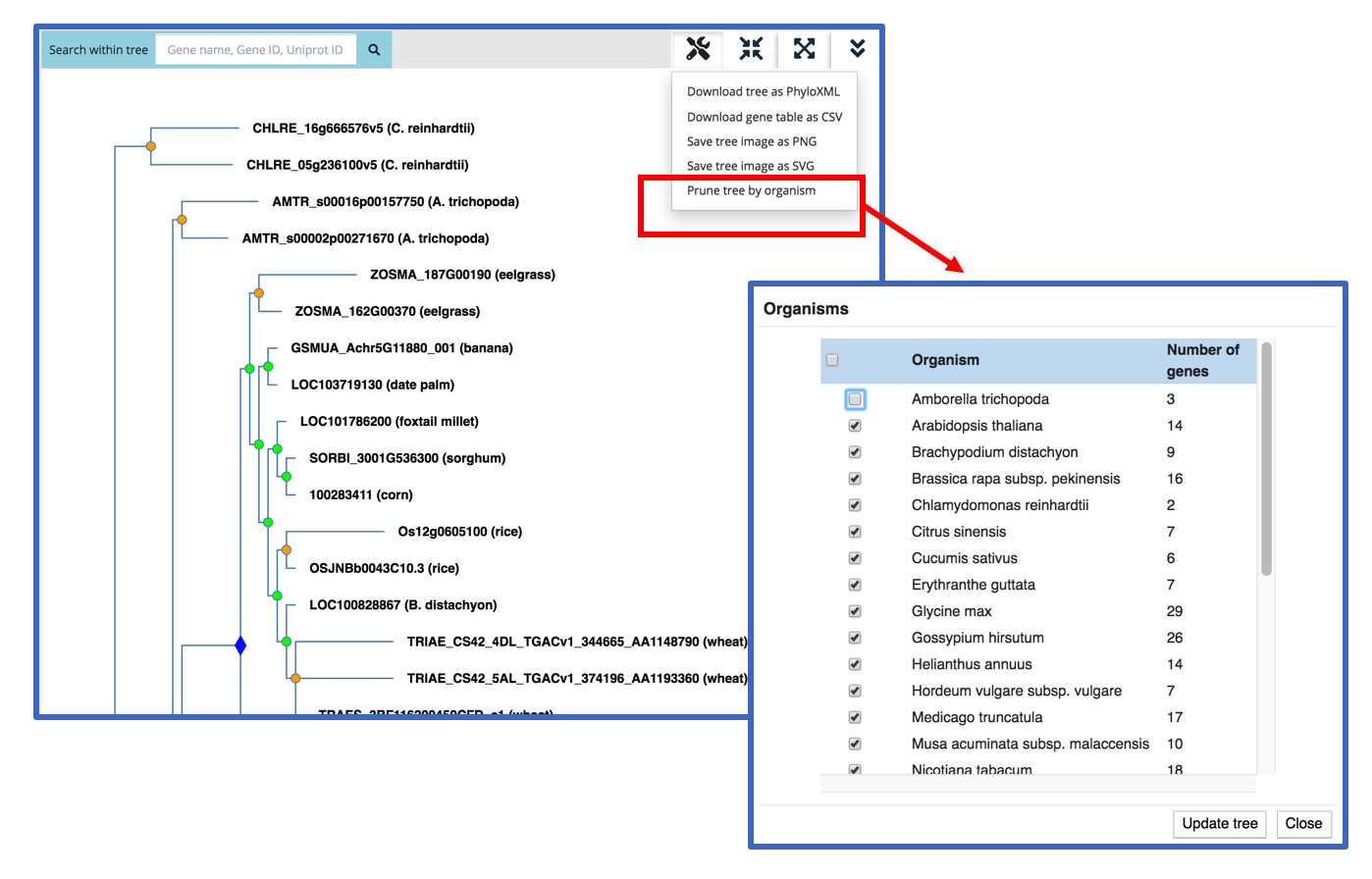
Under the Operations menu choose Prune Tree by Organism. The resulting pop up window will display a list of all the species represented in the current gene tree; by default all of the species are selected. To REMOVE a species (and its genes) from the tree, UNCHECK the box next to the species name. The tree pruning process will remove leaf nodes (genes) of that organism from the tree. The process does not recompute the gene family nor alter the remaining tree.